Dental Crowns: An Essential Guide Under NHS Services
When it comes to restorative dental care, dental crowns are one of the most efficient solutions available. In the context of the NHS (National Health Service), these crowns provide critical support for teeth that are damaged, decayed, or weakened. Understanding the significance of dental crowns can empower patients to make informed decisions about their dental health. This article dives into the world of dental crowns under NHS services and is structured to ensure clarity and comprehensive insight.
What is a Dental Crown?
A dental crown is a cap placed over a tooth to improve its strength, size, shape, or appearance. Crowns are typically recommended when a tooth has been significantly damaged, whether due to decay, injury, or after a root canal procedure. They are essential in stabilizing the tooth structure and ensuring that you can continue to use your teeth comfortably and effectively.
Why Are Dental Crowns Necessary?
Dental crowns serve numerous purposes in dental health:
- Protection: Crowns shield weak teeth from further damage or decay.
- Restoration: They restore the shape and function of severely worn down or broken teeth.
- Aesthetics: Crowns can enhance the appearance of misshapen or discolored teeth.
- Support: They provide support to dental bridges, ensuring stability and comfort.
Types of Dental Crowns Available Under NHS
The NHS offers different types of dental crowns, each with its unique advantages:
1. Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal Crowns
These crowns combine the strength of metal with the aesthetic appeal of porcelain. They are strong and can withstand chewing forces, making them suitable for back teeth.
2. All-Porcelain Crowns
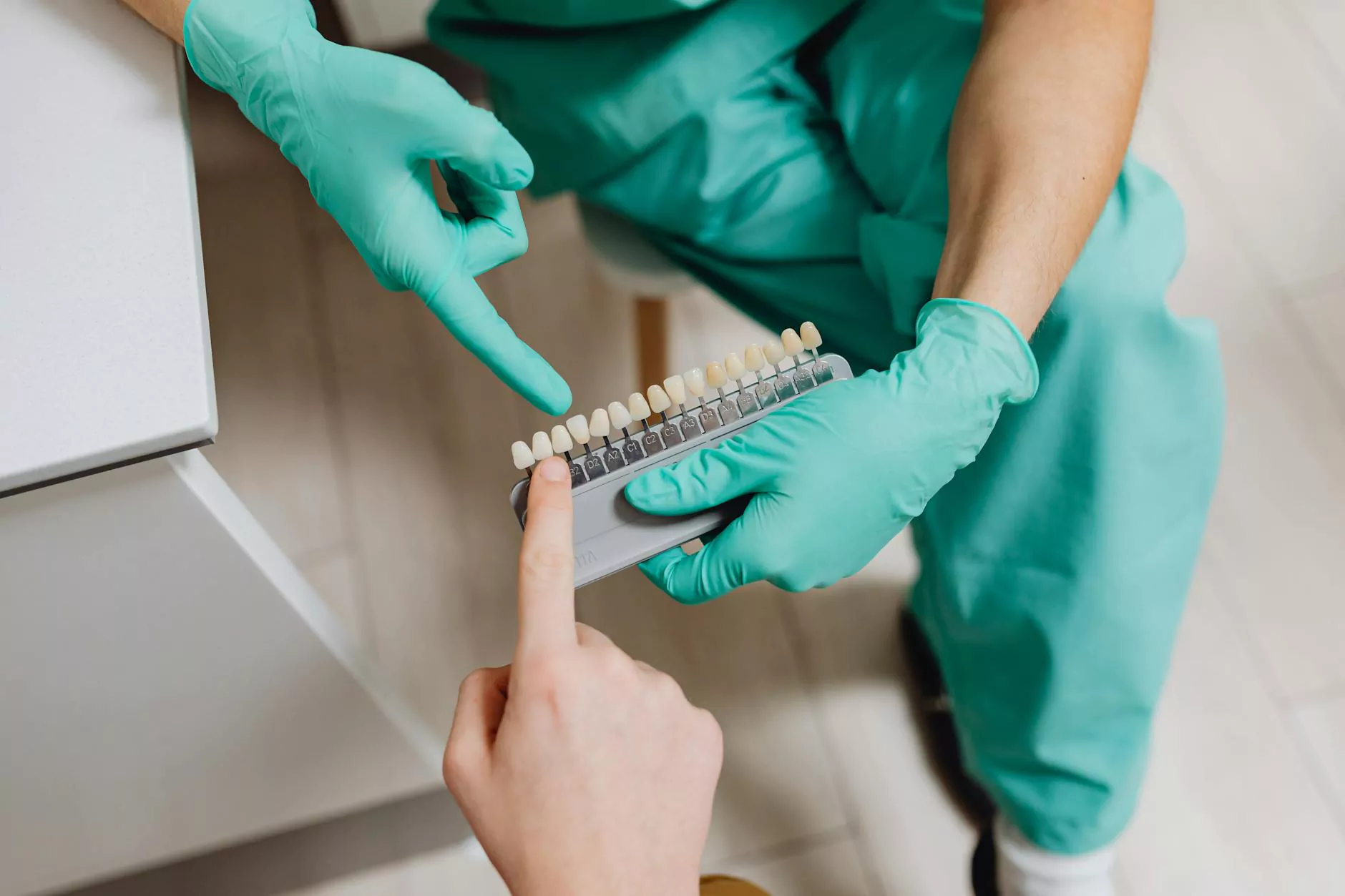
All-porcelain crowns are renowned for their natural appearance. They are often used for front teeth, achieving a seamless blend with existing teeth.
3. Metal Crowns
Metal crowns offer incredible durability and strength. They are often used in the back teeth where the pressure from chewing is more significant.
4. Resin Crowns
These crowns are less common but are a more economical choice. While they mimic the color of natural teeth, they are less durable compared to other options.
The Dental Crown Procedure
Getting a dental crown typically involves a few steps, which can vary slightly depending on individual needs and the type of crown selected:
Initial Consultation
The first step is an initial consultation with your dentist. They will evaluate your dental health, discuss treatment options, and determine if a crown is necessary.
Preparation of the Tooth
Your dentist will begin the procedure by preparing the affected tooth. This process involves:
- Removing any decay and reshaping the tooth to fit the crown.
- Taking impressions of your tooth and the surrounding area.
Creating a Temporary Crown
While the permanent crown is being fabricated (typically takes a couple of weeks), a temporary crown may be placed to protect the tooth.
Fitting the Permanent Crown
Once the permanent crown is ready, you will return to the dentist for its placement. The dentist will check for proper fit and bite before permanently cementing the crown in place.
Costs of Dental Crowns Under NHS
One of the substantial advantages of getting a dental crown through the NHS is the cost-effectiveness. The NHS covers a significant portion of the expense, which can make restorative dental procedures more accessible. However, costs can vary and typically depend on:
- The type of crown selected.
- The complexity of the procedure involved.
- Your specific dental health needs.
To get precise pricing information, it is best to consult with your dentist or the local NHS dental practice.
Benefits of Choosing Dental Crowns
Choosing dental crowns, especially through NHS services, offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Today’s crowns can be matched to the color of your natural teeth.
- Improved Functionality: Crowns restore and enhance the function of damaged teeth.
- Longevity: A well-fitted crown can last many years, making it a wise investment in dental health.
- Support for Other Treatments: Crowns can stabilize bridges and protect weak teeth, contributing to overall dental health.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While dental crowns are generally safe, it is important to be aware of potential risks:
- Sensitivity: Some patients may experience tooth sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures after the procedure.
- Discomfort: Mild discomfort may occur following the placement of the crown.
- Improper Fit: If a crown doesn’t fit properly, it can lead to further dental problems.
Your dentist will provide guidance on how to care for your crown to mitigate these risks.
Caring for Your Dental Crown
After receiving a dental crown, maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial:
- Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste.
- Flossing: Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from around the crown.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Ensure regular visits to your dentist for cleanings and checks.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Be cautious with very hard foods that can damage your crown.
Conclusion
Understanding the significance of dental crowns under NHS services is essential for anyone considering restorative dental care. By learning about the types, procedures, costs, benefits, and care associated with dental crowns, patients can make empowered decisions regarding their oral health. If you are considering a dental crown, consult with a qualified dentist to explore your options and receive tailored advice.
For additional information or to book a consultation, visit wupdoc.com. Your journey to better dental health starts with choosing the right treatment.
dental crown nhs